Fair Value Disclosures
Objective: To explain the logic and configuration of the Fair Value Disclosure Statements as defined by the International Financial Reporting Standards IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement.
Financial Disclosure
Fair Value Measurement has introduced a range of new processes, concepts and financial disclosure requirements when undertaking fair value measurement for an asset or liability.
These concepts include maximizing the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of un-observable inputs.
Fair Value Definition
According to the Australian Accounting Standards Board (AASB), the Fair Value definition is as follows:
'The price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.'
Fair value is a market-based measurement, not an entity-specific measurement. For some assets and liabilities observable market transactions or market information may be available. For other assets and liabilities observable market transactions and market information may not be available. However, the objective of a fair value measurement in both cases is the same – to estimate the price at which an orderly transaction to sell the asset or to transfer the liability would take place between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions (i.e. an exit price at the measurement date from the perspective of a market participant that holds the asset or owes the liability).
Except in the circumstance of an asset held for sale (valued in accordance with AASB5 Assets Held for Sale), the balance of the portfolio is valued in accordance with AASB116 Property Plant and Equipment at Fair Value.
Financial Disclosure Attributes
Assetic records the following attributes (refer to table below) with regards to documenting the valuation inputs and techniques used to determine Fair Value. The disclosures are presented at either the Financial Class or Financial Subclass level.
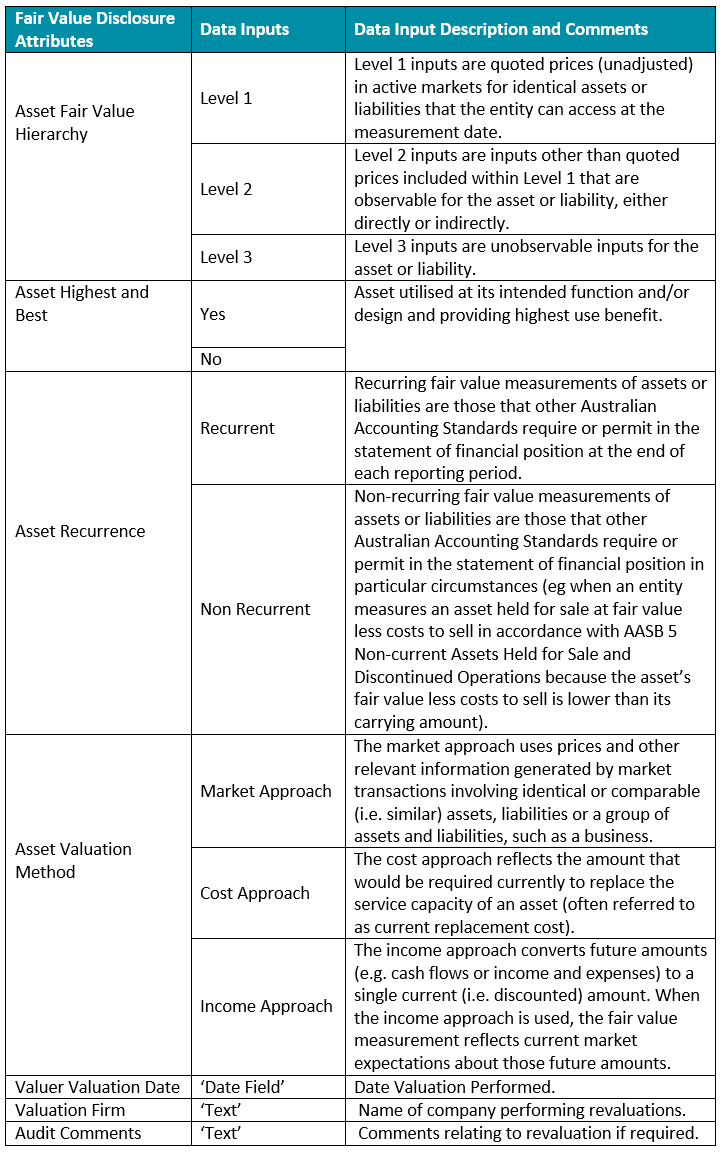
Refer to Assetic Accounting for the ‘step by step’ guide to configure these attributes.
Fair Value Disclosures Report,provides example reports for the Revaluation and Fair Value disclosures:
-
Fair Value Sensitivity Analysis to Un-observable Inputs
-
Analysis of Fair Value Results
-
Comparison to Previous Financial Values
It should be noted that these disclosure statements will be provided to your organization by your valuer.
The content in this guide has been referenced from the IFRS 13 Accounting Standard and AASB 13 Accounting Standard.
Country specific requirements may require additional reporting.
